Elevating Diagnostic Precision at – NewMedd
Understanding PET/CT Scans
NewMedd Diagnostics is a standalone diagnostic imaging facility dedicated to serving patients with comprehensive services. We pride ourselves on offering state-of-the-arttechnology and unmatched quality, all within an all-digital center. Our goal is to providediagnostic imaging services in a serene and comfortable environment, conveniently located and easily accessible to all.We utilize the cutting-edge “GE Discovery IQe 16 slice PET/CT” scanner featuring “light burst detectors” and “Q Clear technology”. This advanced equipment ensures unparalleled and consistent signal-to-noise ratio, enabling precise quantification of metabolic activity for optimal patient outcomes.
Additionally, it allows for the prudentreduction of radiation doses while maintaining diagnostic efficacy. Our facility is also equipped with a dual-head gamma camera, complemented by SPECT capabilities and state-of-the-art quantitation and fusion software, enhancing localization and interpretation accuracy.
This Guide Helps You Understand – PET/CT Scans
- During a single, comprehensive full-body scan lasting approximately 30 minutes, PET captures images revealing subtle metabolic changes in the body due to abnormal cell growth. Simultaneously, CT images aid physicians in precisely identifying the location, size, and shape of diseased tissue or tumors.In essence, PET detects small lesions or tumors, which are then precisely located using CT.Both PET and CT are standard imaging techniques used by physicians to identify the location of cancer within the body before deciding on treatment.
- PET scans are highly sensitive, detecting the metabolic signals of actively growing cancer cells. On the other hand, CT scans provide detailed images of internal anatomy, revealing the location, size, and shape of abnormal cancerous growths. While each imaging test has its own advantages and limitations, when the results of PET and CT scans are combined or "fused," the resulting image offers comprehensive information on cancer location and metabolism. The key takeaway is that both PET and CT scans can be performed simultaneously.
How Does – It Work?
- In PET/CT imaging, while CT scans offer detailed anatomical information like tumor size and location, PET scans reveal metabolic details such as cellular activity within the tumor mass. Together, PET/CT offers superior accuracy compared to standalone PET or CT scans.
- Anatomical details are obtained through CT scanners, which emit X-rays through thebody, measured by detectors, and processed by computer algorithms to create images of internal structures.

- Metabolic details are captured through PET scans using FDG, a glucose analog tagged with the radionuclide F18. Metabolically active tissues or tumors, consuming glucose athigher rates, emit positrons as the tagged sugar decays. These positrons collide with electrons, emitting gamma rays, which are converted into images by a computer. These images highlight metabolic "hot spots," often indicative of rapidly growing tumors.
- The entire procedure typically lasts under 30 minutes, delivering comprehensive diagnostic insights to healthcare providers swiftly. PET/CT systems ensure exceptional image quality and diagnostic accuracy.
What PET/CT – Scans Detect

Breast Cancer
A PET scan helps in detecting breast cancer by identifying malignant tumors, assessing the stage of cancer, and evaluating the effectiveness of treatment. It highlights areas of high metabolic activity where cancer cells may be
present, aiding in precise localization and potential metastasis tracking.
Esophageal Cancer
In esophageal cancer, a PET scan detects the presence of tumors in the esophagus and assesses whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs. It helps in staging the cancer, planning treatment, and
monitoring response to therapies.
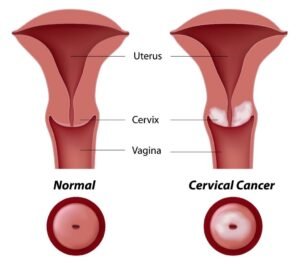
Cervical Cancer
PET scans in cervical cancer are used to detect the primary tumor in the cervix, evaluate lymph node involvement, and identify metastases. It provides detailed images that help in staging the disease, guiding biopsies, and planning
radiation therapy.
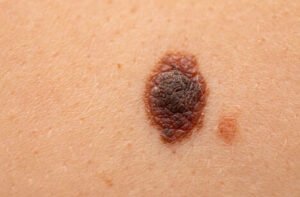
Melanoma
For melanoma, PET scans detect the spread of cancerous cells to lymph nodes and other organs. It is particularly useful for staging advanced melanoma,checking for recurrence, and guiding treatment decisions by highlighting areas of
abnormal metabolic activity.
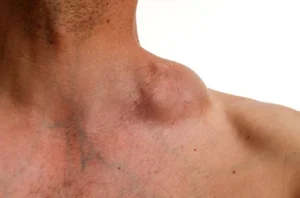
Lymphoma
PET scans are crucial in diagnosing and staging lymphoma by revealing the extent of lymph node involvement and detecting cancer in other organs. They help in evaluating the effectiveness of treatment and in monitoring for potential relapse by identifying active disease sites.
Lung Cancer
In lung cancer, PET scans detect malignant tumors, assess lymph node involvement, and identify distant metastases. They provide detailed images that help in staging the cancer, planning treatment, and evaluating the response to
therapies.
Colorectal Cancer
PET scans for colorectal cancer detect primary tumors, assesslymph node involvement, and identify metastases, particularly in the liver and lungs.They are used in staging the disease, planning surgery or radiation therapy, and
monitoring for recurrence.
Head and Neck Cancer
For head and neck cancers, PET scans detect primary tumors, assess the extent of the disease, and evaluate lymph node involvement. They help in staging the cancer, planning treatment, and monitoring the effectiveness of
therapies.

Ovarian Cancer
PET scans in ovarian cancer detect tumors, assess the spread of the disease within the pelvic region and to distant organs, and evaluate lymph node involvement. They are used for staging, guiding treatment decisions, and monitoring the
response to therapy.
Applications of – PET/CT
- Determining the extent of disease
- Identifying disease location for biopsy, surgery, or treatment planning
- Assessing response to and efficacy of treatments
Advantages of – PET/CT
- Earlier Detection
- Accurate Staging and Localization
- Precise Treatment Planning and Monitoring
The integration of PET and CT technologies– offers numerous benefits
- Timely Diagnosis
- Precise Tumor Localization
- Enhanced Treatment Strategies
- Improved Monitoring of Disease Progression
The advanced imaging capabilities of PET/CT scanners enhance patient outcomes by providing clinicians with comprehensive insights into both the anatomical and metabolicaspects of the disease. Additionally, PET/CT facilitates early detection of cancer recurrence, even in cases where tumors may be obscured by scar tissue resulting from prior surgeries or radiation therapy, particularly in the head and neck region.
Previously, interpreting separate CT and PET scans performed at different times and
locations posed challenges due to changes in the patient’s body position. However, with the combined PET/CT approach, physicians gain a holistic understanding of the body’s anatomical and metabolic status simultaneously, streamlining diagnosis and treatment planning.
What to – Expect
- When faced with challenging questions, waiting for answers isn't always an option. A PET scan offers clarity in such situations.
- Unlike x-rays, CT scans, or MRIs which provide images of bones, organs, and tissues, a PET scan provides insight into how your body's cells are functioning.
- This scan aids you and your physician in making well-informed decisions regarding your diagnosis and treatment plan.

Preparing for – Your Scan
- Dress comfortably and warmly, as scanner rooms can be cool.
- Avoid eating for at least four to six hours prior to your scan, including sugar-free gum, mints, candy, and non-water beverages.
- Refrain from strenuous exercise on the day of your exam.
- Bring copies of your most recent CT, x-ray, or MRI films with you on the day of your PET scan.
- Expect to lie still for 30-75 minutes during the scan procedure.
The Procedure
A PET scan is painless and has no side effects. After fasting for 6 hours, you'll receive a trace amount of radioactive glucose through injection, which spreads throughout your body.
Duration of the Scan
The scan typically lasts 1-2 hours, depending on its type and the scanner used. Trained nuclear medicine physicians or radiologists interpret the results, which are then shared with your referring physician.
For Diabetics
Diabetic patients should contact the facility for special instructions.
Post-Scan Instructions
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day after the PET scan.
Patient – Instructions
- Fasting for 6-8 hours is recommended for optimal scan results.
- Hydration is encouraged.
- Patients with prolonged fasting or discomfort due to an empty stomach can consume cucumber or plain tomato juice after specific instructions from the nuclear medicine staff.
- Diabetic patients, especially those with morning appointments, should inquire about personalized instructions.
- Pre-menopausal patients should inform the nuclear medicine doctor about their menstrual cycles if expected during the scheduled scan.
- Serum creatinine levels should be tested within a week before the scheduled PET-CT scan.
- Patients scheduled for PET cardiac or brain scans should adhere to specific dietary and fasting guidelines.
- Bring all previous medical reports and CDs of previous PET scans, if available.
- Consult the radiation safety officer for precautions during and after the procedure.