- NewMedd Diagnostics: 59, 3d Cross, Yadavagiri, Near Sunanda School, Mysuru
Nuclear Medicine
What is Nuclear Medicine?
Nuclear Medicine (NM) is a specialized medical imaging technique that utilizes small amounts of radioactive isotopes attached to molecules or chemicals, known as radiopharmaceuticals. These radiopharmaceuticals, once administered to the patient, localize within specific organs and organ systems and emit photons, which are then detected by sophisticated equipment called Gamma Cameras. Unlike conventional imaging modalities, such as x-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, Nuclear Medicine provides functional information, including physiological, pathological, molecular, and metabolic details of various tissues and organs within the body.
In addition to diagnosis, Nuclear Medicine also encompasses several therapeutic applications, notably in the treatment of hyperthyroidism, thyroid cancers, advanced neuroendocrine tumors, bone pain resulting from cancer metastasis, and inflammatory joint disorders.
How is the Procedure Conducted?
The procedure typically involves intravenous administration of the radiopharmaceutical. Depending on the type of study, scanning may occur immediately or after a certain period following the administration of the radiotracer. Various images or serial scans may be required in some cases.
What is Nuclear Medicine?
- Women should inform their physician or technologist if there is any possibility of pregnancy or if they are breastfeeding.
- Most scans do not require specific preparation such as fasting or refraining from passing urine, except for specific cases like myocardial perfusion scans, gallbladder ejection studies, and PET/CT scans, where overnight fasting is necessary. Patients receive specific instructions for such cases.
- The duration of the scans typically ranges from 30 minutes to 6 hours, depending on the type of scan and additional imaging requirements. In some cases, delayed images may be taken after 24 hours if necessary.
- During the scan, patients lie on a couch under the gamma camera. Several views may be required, with each lasting from 5 to 15 minutes. SPECT studies involve the scanning machine moving around the patient's body, providing images without causing any discomfort.
Safety of Nuclear Medicine Procedures
- The doses of radiotracers administered are minimal, and the resulting radiation exposure is outweighed by the benefits of the procedure. The radiation exposure from a nuclear medicine procedure is comparable to a few days of background radiation that everyone receives and is often lower than conventional imaging modalities like IVP, CT, or angiograms.
- Allergic reactions to radiopharmaceuticals are extremely rare and usually mild if they occur.
- Patients do not experience any adverse effects from the administration of radiotracers or the scanning procedure and can resume normal activities immediately afterward in most cases.
General Instructions
- Patients are advised to bring their previous medical records as nuclear medicine scans may need to be tailored to specific situations, requiring correlation with other studies.
- Jewelry and metallic accessories should be left at home or removed before the exam to avoid interference with the procedure.
- It is recommended to bring only one attendant, and pregnant women or small children should not accompany the patient
- The results of the study may take 1 to 6 hours to be dispatched, and may take longer in some cases.
Different Types of Nuclear Medicine Studies
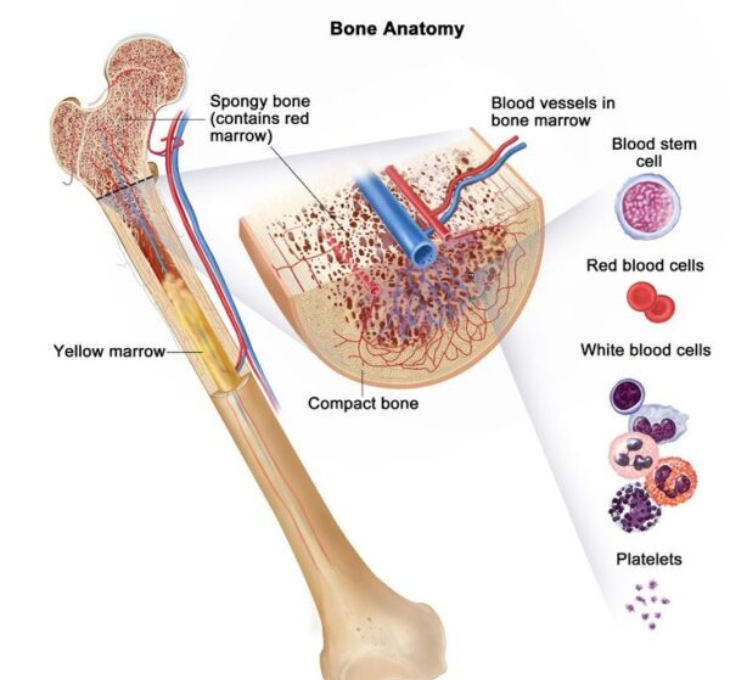
Bone Scan
Detects bone cancer, tumors, fractures, or infections. No special preparations are required.
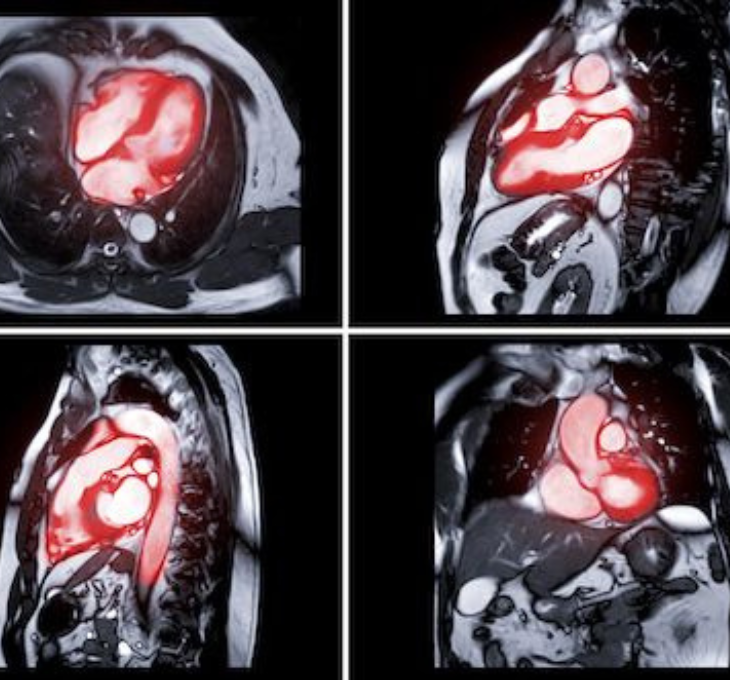
Myocardial Perfusion (Heart) Scan
Provides a three-dimensional image of the heart to assess blood flow under stress and resting conditions. Special instructions are provided for this study, and patients may remain in the department for up to five or six hours.

Brain SPECT/PET
Evaluates blood flow in different brain areas and aids in the diagnosis of dementia, stroke, headaches, or seizures.
Lung Scan
Demonstrates blood supply to the lungs and helps detect blood flow obstructions, such as pulmonary embolism.
Kidney and Bladder Scan
Evaluates kidney function, blood flow to each kidney, and detects urinary flow abnormalities.
Thyroid Scan
Assesses thyroid gland function, especially hyperactivity.
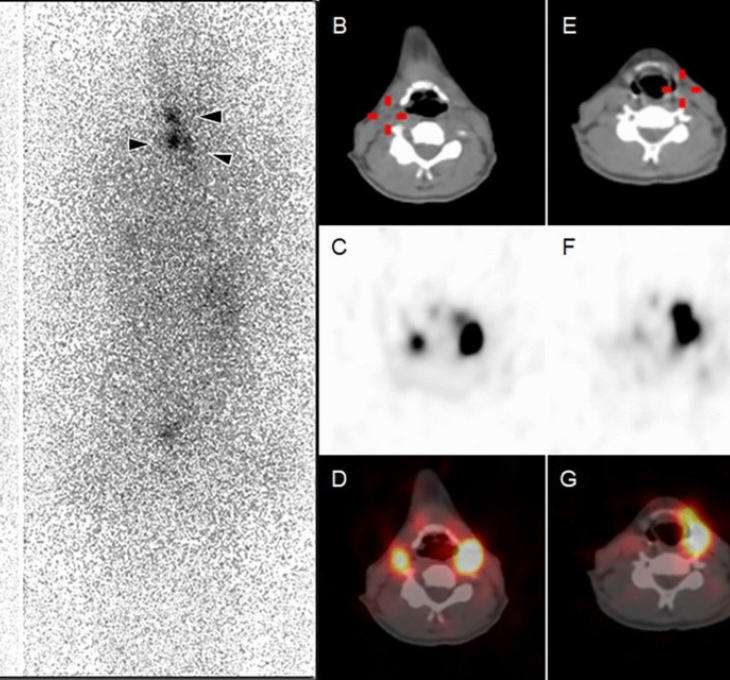
I-131 Scan
Performed in thyroid cancer patients after thyroid surgery or during follow-up.
Parathyroid Scan
Used to identify parathyroid gland abnormalities causing elevated calcium levels.
GI Bleed (Red Cell) Scan
Localizes gastrointestinal bleeding sites for appropriate treatment.
Hepatobiliary Study
Obtains liver and gallbladder images to diagnose liver dysfunction, gallbladder inflammation, etc.
